Technology
LPWAN — Low-Power Wide-area Network
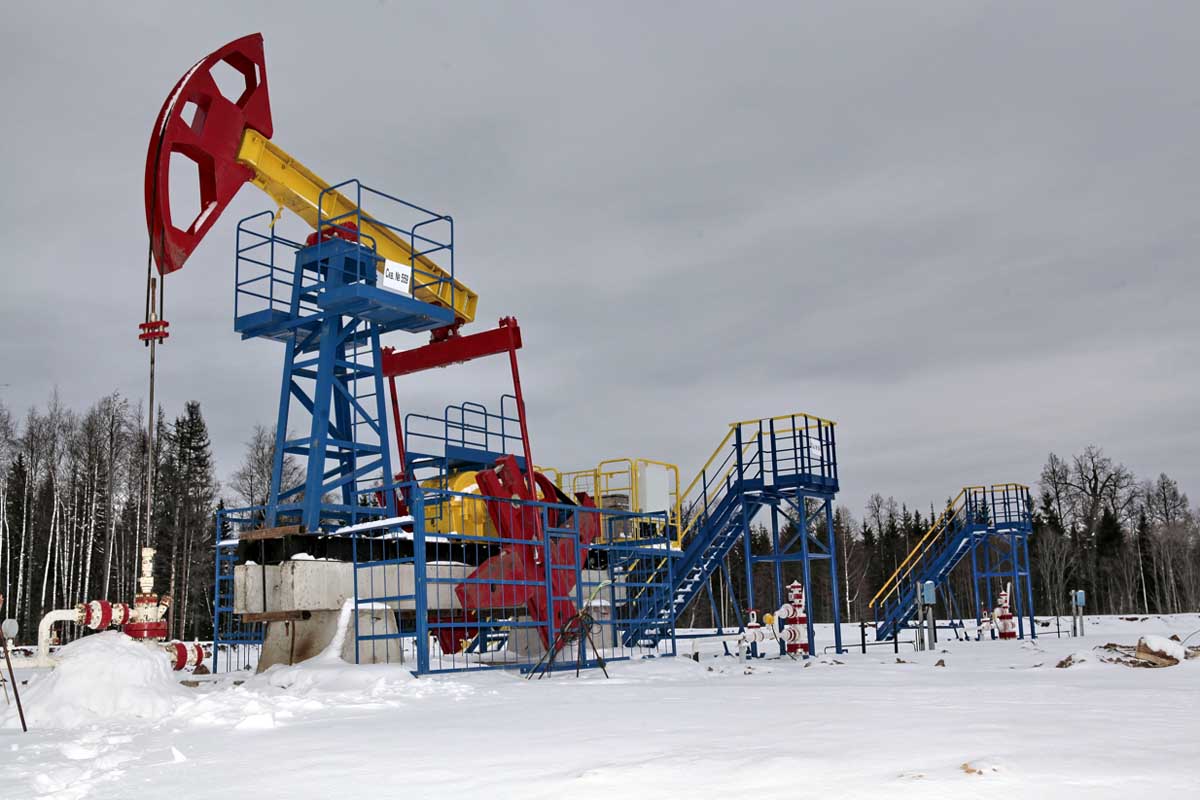
LPWAN is a wireless technology for long-range transmission of small data, designed for distributed telemetry networks, machine-to-machine communication and the Internet of things.

ROSSMA is a member of the international community of equipment producers according to LoRaWAN standard – LoRa Alliance.

How it works
The basis of data transmission technology LPWAN principle at the physical level is the property of radio systems — energy increase, and hence the range of communication with a decrease in transmission speed. The lower the bit speed, the more energy is used in each bit and the easier it is to isolate it against the background noise in the receiving part of the system. Thus, low speed of data transmission allows to achieve greater range of their reception.
The approach used to build an LPWAN network is similar to the way mobile networks work. The LPWAN network uses a star topology where each device communicates directly with the base station.
A device or modem with an LPWAN module transmits data over a radio channel to the base station. The station receives signals from all devices within its range, and transmits to a remote server using an available communication channel: Ethernet, cellular, VSAT.
The data obtained on the server is used for display, analysis, reporting and decision-making.
Device management, software update occurs with the help of the reverse communication channel.

Application
The LPWAN technology is focused on the applications that require guaranteed transmission of a small amount of data, the possibility of long-term operation of network devices from autonomous power sources, large territorial coverage of the wireless network. The main areas of application of the LPWAN technology are wireless sensor networks, automatisation of meter readings, industrial monitoring and control systems.
The long range of radio signal transmission in comparison with other wireless technologies used for GPRS or ZigBee telemetry reaches 45 km.
Low power consumption of end devices, because of the minimum energy costs for the transmission of a small data package.
No need to obtain a frequency resolution and a fee for the radio frequency spectrum, due to the use of non-licensed frequencies (relevant only for the Lorawan standard).
High penetrating capacity of radio signal.
Highly-scalable
The main competitive characteristics
Large coverage range and easy network deployment
Allows subscribers to carry out data transmission over distances greater than the network of base stations of GSM standard. Coverage is created specifically for the client's tasks. Not licensed frequency range.

Comparison
-
LoRaWAN
Spectrum Unlicensed(ISM) Who supports LoRa Alliance (IBM, Cisco, Semtech, Bouygues Telecom) Speed 0.3 — 15 Kbps Bandwidth 200 kHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +20 dB Frequency re-use 1 Private network support yes Module autonomy 20 years Availability Available -
NB-LTE-M (NB-IoT)
Spectrum Licensed, 2G Who supports Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, Qualcomm, Alcatel etc. Speed < 150 Kbps Bandwidth 200 kHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +20 dB Frequency re-use 7, 9 — for 2G, 1 — for LTE Private network support No Module autonomy 10 years Availability Standard: 2Q 2016 Commerce: 2018 -
NB-CIoT
Spectrum New (Clean state) narrow band spectrum, not used Who supports Huawei, Vodafone Speed < 50 Kbps Bandwidth 200 kHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +20 dB Frequency re-use 12 — for 2G, 1 — for LTE Private network support No Module autonomy 10 years Availability Standard: 2Q 2016 Commerce: 2018 -
LTE-M
Spectrum On an existing LTE network Who supports Ericsson, Nokia, Intel… Speed < 1 Mbit/s Bandwidth 1.4 MHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +0 dB Frequency re-use 1 Private network support No Module autonomy Several months Availability Standard: 2Q 2016 Commerce: 2018
Problems that can be solved using LoRaWan
Absence of power supply for sensors and measuring devices in "field».
Absence of GSM networks coverage (or unsatisfactory coverage) for data transmission. There is no communication.
Heterogeneity of interfaces for data collection from control and measuring devices (CMD) and automatic controllers.
Expensive installation of wire lines for control and measuring devices connection (control and electric cables).
NB-IoT — Narrow Band Internet of Things
NB-IoT is the standard of cellular communication for telemetry devices with low volumes of data exchange.
It is intended for connection to digital communication networks of a wide range of autonomous devices. For example, medical sensors, resource consumption meters, smart home devices, etc.
It is mainly used in urban areas with high density coverage of cellular networks GSM. In everyday life, such communication systems are called the Internet of things.
NB-IoT is one of three IOT standards developed by 3GPP for cellular networks: eMTC (enhanced Machine-Type Communication), NB-IoT and EC-GSM-IoT. eMTC. has the highest capacity and takes place on the LTE equipment.
NB-IoT network can be deployed on the equipment of cellular networks LTE, as well as separately, including on top of GSM. EC-GSM-IoT provides the lowest bandwidth and is deployed above GSM networks.
flexible power consumption control of devices (up to 10 years in a network from the battery with the capacity of 5 W*h)
huge network capacity (tens-hundreds of thousands of connected devices per base station)
signal modulation optimized to improve the sensitivity
low cost of devices
Comparison
-
LoRaWAN
Spectrum Unlicensed(ISM) Who supports LoRa Alliance (IBM, Cisco, Semtech, Bouygues Telecom) Speed 0.3 — 15 Kbps Bandwidth 200 kHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +20 dB Frequency re-use 1 Private network support yes Module autonomy 20 years Availability Available -
NB-LTE-M (NB-IoT)
Spectrum Licensed, 2G Who supports Ericsson, Nokia, Intel, Qualcomm, Alcatel etc. Speed < 150 Kbps Bandwidth 200 kHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +20 dB Frequency re-use 7, 9 — for 2G, 1 — for LTE Private network support No Module autonomy 10 years Availability Standard: 2Q 2016 Commerce: 2018 -
NB-CIoT
Spectrum New (Clean state) narrow band spectrum, not used Who supports Huawei, Vodafone Speed < 50 Kbps Bandwidth 200 kHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +20 dB Frequency re-use 12 — for 2G, 1 — for LTE Private network support No Module autonomy 10 years Availability Standard: 2Q 2016 Commerce: 2018 -
LTE-M
Spectrum On an existing LTE network Who supports Ericsson, Nokia, Intel… Speed < 1 Mbit/s Bandwidth 1.4 MHz Improving the energy budget of the GSM +0 dB Frequency re-use 1 Private network support No Module autonomy Several months Availability Standard: 2Q 2016 Commerce: 2018
Perm
Russia
614064


